Four Main Groups of Microorganisms
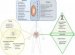
In biology, there are four distinguishable types of microorganisms. These organisms are proven to be harmful or helpful to humans, plants and animals alike.
A virus (singular) or viruses (plural) are a group of sub microscopic pathogens that can only replicate inside the living cells of organisms. Viruses infect all types of organisms, from animals and plants to bacteria and archaea.
Viruses are unique because they exhibit some of the activities that are common to organic life, but they are missing many of the others.
A bacterium (singular) or bacteria (plural) are a large group of prokaryotic microorganisms. They are typically several micrometres in length, and are found in a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals.
A fungus (singular) or fungi (plural) are a large group of eukaryotic organisms that include microorganisms such as yeasts and moulds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms.
One major difference of fungus compared to other microorganisms is that fungal cells have cell walls that contain chitin, unlike the cell walls of plants, which contain cellulose.
A protozoon (singular) or protozoans (plural) are a diverse group of single-cell eukaryotic organisms, many of which are motile. Throughout history, protozoa have been defined as single-cell protists with animal-like behaviour, e.g., movement.
1. Bacteria are unicellular organisms. They are classified as prokaryotic because they lack a nucleus.
2. The three major basic shapes of bacteria are bacillus, coccus, and spiral.
3. Most bacteria have a peptidoglycan cell wall; they divide by binary fission; and they may possess flagella.
4. Bacteria can use a wide range of chemical substances for nutrition (obtained via absorption).
In biology, there are four distinguishable types of microorganisms. These organisms are proven to be harmful or helpful to humans, plants and animals alike.
A virus (singular) or viruses (plural) are a group of sub microscopic pathogens that can only replicate inside the living cells of organisms. Viruses infect all types of organisms, from animals and plants to bacteria and archaea.
Viruses are unique because they exhibit some of the activities that are common to organic life, but they are missing many of the others.
A bacterium (singular) or bacteria (plural) are a large group of prokaryotic microorganisms. They are typically several micrometres in length, and are found in a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals.
A fungus (singular) or fungi (plural) are a large group of eukaryotic organisms that include microorganisms such as yeasts and moulds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms.
One major difference of fungus compared to other microorganisms is that fungal cells have cell walls that contain chitin, unlike the cell walls of plants, which contain cellulose.
A protozoon (singular) or protozoans (plural) are a diverse group of single-cell eukaryotic organisms, many of which are motile. Throughout history, protozoa have been defined as single-cell protists with animal-like behaviour, e.g., movement.
-
1. Bacteria are unicellular organisms. They are classified as prokaryotic because they lack a nucleus.
2. The three major basic shapes of bacteria are bacillus, coccus, and spiral.
3. Most bacteria have a peptidoglycan cell wall; they divide by binary fission; and they may possess flagella.
4. Bacteria can use a wide range of chemical substances for nutrition (obtained via absorption).
Minor edit?
34 people found this useful
Was this answer useful?