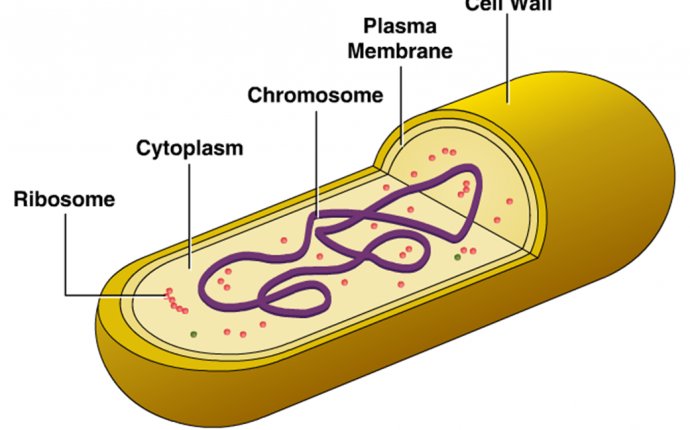
Parts of a Typical Bacterial cell
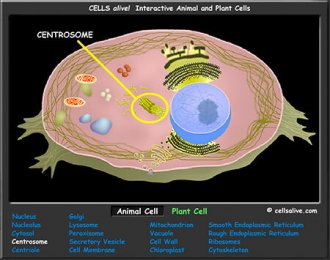 Living cells are divided into two types - prokaryotic and eukaryotic (sometimes spelled procaryotic and eucaryotic). This division is based on internal complexity. The following interactive animations provide graphic roadmaps to the organization of both of these cell types.
Living cells are divided into two types - prokaryotic and eukaryotic (sometimes spelled procaryotic and eucaryotic). This division is based on internal complexity. The following interactive animations provide graphic roadmaps to the organization of both of these cell types.
Prokaryotic Cell Model
For life all cells have basic needs. Cells have diverged in their structure and function to accommodate these survival requirements. Here are some KEY TERMS to help you think, explore and search for similarities and significant differences that have become the characteristics of eukaryote (animal, plant) and prokaryotic (bacteria) cells. Examples might be searching: eukaryote prokaryote reproduction or animal plant cell energy.
- Reproduction / cell division
- Energy trapping, storage and consumption
- Form / shape / structure
- Cell specialization
- Compartmentalization of cell functions
- Communication within and beyond the cell